REFERENCES
- [1] X. Chen, Z. Cui, M. Fan, P. Vitousek, M. Zhao,W. Ma, Z.Wang,W. Zhang, X. Yan, J. Yang, et al., (2014) “Producing more grain with lower environmental costs" Nature 514(7523): 486–489. DOI: 10.1038/nature13609.
- [2] N. D. Mueller, L. Lassaletta, B. C. Runck, G. Billen, J. Garnier, and J. S. Gerber, (2017) “Declining spatial efficiency of global cropland nitrogen allocation" Global Biogeochemical Cycles 31(2): 245–257. DOI: 10.1002/2016GB00551.
- [3] M. Hvistendahl. China’s push to add by subtracting fertilizer. 2010. DOI: 10.1126/science.327.5967.801.
- [4] X. Ma, J. Chen, Y. Yang, X. Su, S. Zhang, B. Gao, and Y. C. Li, (2018) “Siloxane and polyether dual modification improves hydrophobicity and interpenetrating polymer network of bio-polymer for coated fertilizers with enhanced slow release characteristics" Chemical Engineering Journal 350: 1125–1134. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.061.
- [5] G. Akay, (2017) “Sustainable ammonia and advanced symbiotic fertilizer production using catalytic multireaction-zone reactors with nonthermal plasma and simultaneous reactive separation" ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 5(12): 11588–11606. DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02962.
- [6] Y. Yang, X. Ni, Z. Zhou, L. Yu, B. Liu, Y. Yang, and Y. Wu, (2017) “Performance of matrix-based slow-release urea in reducing nitrogen loss and improving maize yields and profits" Field crops research 212: 73–81. DOI: 10.1016/j.fcr.2017.07.005.
- [7] S. Li, Y. Lei, Y. Zhang, J. Liu, X. Shi, H. Jia, C.Wang, F. Chen, and Q. Chu, (2019) “Rational trade-offs between yield increase and fertilizer inputs are essential for sustainable intensification: A case study in wheat–maize cropping systems in China" Science of the Total Environment 679: 328–336. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.085.
- [8] Y. Sun, R. Hu, and C. Zhang, (2019) “Does the adoption of complex fertilizers contribute to fertilizer overuse? Evidence from rice production in China" Journal of Cleaner Production 219: 677–685. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.118.
- [9] L. Zhang, X. Li, J. Yu, and X. Yao, (2018) “Toward cleaner production: what drives farmers to adopt ecofriendly agricultural production?" Journal of cleaner production 184: 550–558. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.272.
- [10] A. M. Senna, J. B. do Carmo, J. M. S. da Silva, and V. R. Botaro, (2015) “Synthesis, characterization and application of hydrogel derived from cellulose acetate as a substrate for slow-release NPK fertilizer and water retention in soil" Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 3(2): 996–1002. DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2015.03.008.
- [11] J. Lynch, (1995) “Root architecture and plant productivity." Plant physiology 109(1): 7. DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.1.7.
- [12] X. Du, C. Liu, M. Jiang, and H. Yuan, (2022) “Design and development of fertilizer point-applied device in rootzone" Applied Engineering in Agriculture: 0. DOI: 10.13031/aea.14846.
- [13] L. Zhang, H. Song, X. Chen, D. Lu, and H. Wang, (2020) “Primary study on nutrient migration under hole fertilization in soils" Soils 52(6): 1145–1151. DOI: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2020.06.007.
- [14] R. Adu-Gyamfi, S. Agyin-Birikorang, I. Tindjina, S. M. Ahmed, A. D. Twumasi, V. K. Avornyo, and U. Singh, (2019) “One-time fertilizer briquettes application for maize production in Savanna agroecologies of Ghana" Agronomy Journal 111(6): 3339–3350. DOI: 10.2134/agronj2019.04.0292.
- [15] R. Adu-Gyamfi, S. Agyin-Birikorang, I. Tindjina, Y. Manu, and U. Singh, (2019) “Minimizing nutrient leaching from maize production systems in northern Ghana with one-time application of multi-nutrient fertilizer briquettes" Science of the Total Environment 694: 133667. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133667.
- [16] C. Jiang, D. Lu, C. Zu, J. Shen, S. Wang, Z. Guo, J. Zhou, and H. Wang, (2018) “One-time root-zone N fertilization increases maize yield, NUE and reduces soil N losses in lime concretion black soil" Scientific Reports 8(1): 1–10. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-28642-0.
- [17] C. Jiang, D. Lu, C. Zu, J. Zhou, and H.Wang, (2018) “Root-zone fertilization improves crop yields and minimizes nitrogen loss in summer maize in China" Scientific Reports 8(1): 1–9. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-33591-9.
- [18] C. Jiang, X. Ren, H.Wang, D. Lu, C. Zu, and S.Wang, (2019) “Optimal nitrogen application rates of one-time root zone fertilization and the effect of reducing nitrogen application on summer maize" Sustainability 11(10):2979. DOI: 10.3390/su11102979.
- [19] Z. Junxiong, L. Huameng, G. Jin, L. Zehong, and C. Ying, (2018) “Simulation and test of corn layer alignment position hole fertilization seeder based on SPH" Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery 49(9): DOI: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.09.007.
- [20] W. Nan, L. Jing, and L. Baofa, (2018) “Design and test on no-tillage planter precise hole fertilization system" Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery 49(7): DOI: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.07.008.
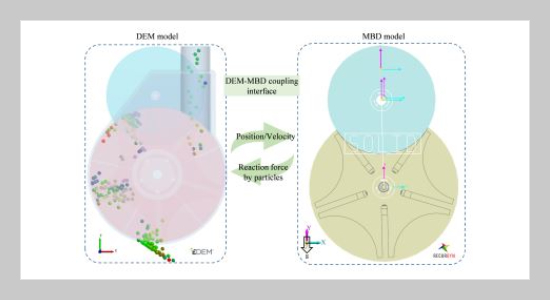
- [21] Z. Chen, D. Xue, G. Wang, D. Cui, Y. Fang, and S. Wang, (2021) “Simulation and optimization of the tracked chassis performance of electric shovel based on DEM-MBD" Powder Technology 390: 428–441. DOI:10.1016/j.powtec.2021.05.085.
- [22] L. Cailing, W. Dan, S. Jiannong, L. Yanni, D. Xin, and Z. Fuyin, (2018) “Systematic study on boundary parameters of Discrete Element Simulation of granular fertilizer" Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery 49(9): DOI: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.09.009.
- [23] Q. Zhu, G.Wu, L. Chen, C. Zhao, and Z. Meng, (2018) “Influences of structure parameters of straight flute wheel on fertilizing performance of fertilizer apparatus" Transactions of the CSAE 34(18): 12–20. DOI: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.18.002.
- [24] S. Ding, L. Bai, Y. Yao, B. Yue, Z. Fu, Z. Zheng, and Y. Huang, (2018) “Discrete element modelling (DEM) of fertilizer dual-banding with adjustable rates" Computers and electronics in agriculture 152: 32–39. DOI: 10.1016/j.compag.2018.06.044.