Jung-Tang Huang This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1, Shih-Hung Chan1 and Shao-Yi Hou2 1Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei, Taiwan 106, R.O.C.
2Dept. of Chemical Engineering, National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei, Taiwan 106, R.O.C.
Received:
February 15, 2007
Accepted:
October 22, 2007
Publication Date:
June 1, 2008
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2008.11.2.05
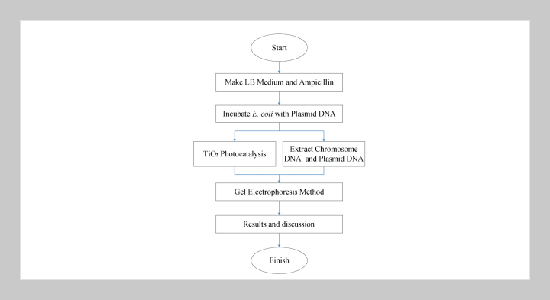
This paper mainly studies the photocatalysis effects of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles on the decomposition of E. coli (Escherichia coli) cells. We utilize the Gel Electrophoresis technology to determine the situation of E. coli cells that were decomposed by photocatalysis using ultraviolet radiation. According to the distribution of Plasmid DNA and chromosome DNA on agaroses, we could grade the destruction level caused by both photocatalysis and ultraviolet radiation. After the UV illumination on E. coli cells for one, two and three days, we discovered that ultraviolet radiation could destroy E. coli cells and also decompose Plasmid DNA and chromosome DNA. Furthermore, the results of many experiments showed repeatedly and regularly that if we use both ultraviolet radiation and suitable quantity of TiO2 nanoparticles on photokilling of E. coli cells, plasmid DNA and chromosome DNA could be decomposed more seriously than only using UV radiation.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Titanium Dioxide, Photocatalysis, E. coli Cells, Gel Electrophoresis Technique, Agaroses
REFERENCES