Ming-Hwa R. Jen This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1, Yu-Chung Tseng1 and Chun-Hsien Wu1 1Department of Mechanical and Electro-Mechanical Engineering National Sun Yat-Sen University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan 804, R.O.C.
Received:
January 6, 2004
Accepted:
May 3, 2004
Publication Date:
September 1, 2004
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2004.7.3.07
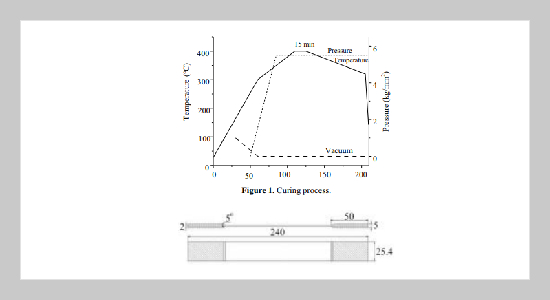
This work mainly aims to manufacture nanocomposite laminates at first. The prepreg AS-4 graphite/PolyEtherEtherKetone laminates were used to make a 16-layered APC-2 laminate of 2 mm thick via curing the modified diaphragm. The nanoparticles of Silica (SiO2) were uniformly spread on the specific interfaces totally about 1-3% by weight of a laminate by sol-gel method. Second, by the results of mechanical testing we found that the optimal content of nanoparticles is 1% of weight percentage, and the ultimate strength increases with 10% and the corresponding stiffness increases with 22% in the quasi-isotropic nanocomposite laminates. At elevated temperature, the ultimate strength and the stiffness of the mechanical properties drop slightly below 75 ºC. and degrade highly at 150 ºC.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Nanoparticles, Composite, Laminate, Mechanical Property, Tensile Test.
REFERENCES