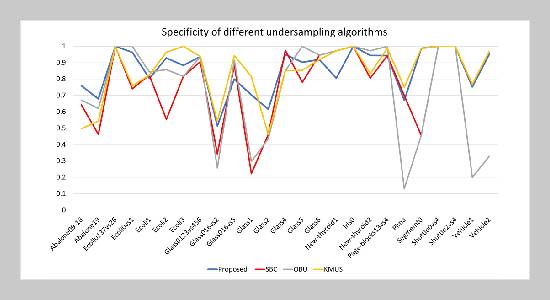
- [1] M. M. R. Henein, D. M. Shawky, and S. K. Abd-ElHafiz, (2018) “Clustering-based Under-sampling for Software Defect Prediction" Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Software Technologies: 219–227. DOI: 10.5220/0006911402190227.
- [2] Y. SUN, A. K. C. WONG, and M. S. KAMEL, (2009) “CLASSIFICATION OF IMBALANCED DATA: A REVIEW" International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence 23: 687–719. DOI: 10.1142/S0218001409007326.
- [3] M. Wang, X. Yao, and Y. Chen, (2021) “An ImbalancedData Processing Algorithm for the Prediction of Heart Attack in Stroke Patients" IEEE Access 9: 25394–25404.
- [4] Vibha and A. P. Singh. Analysis of Variants of KNN Algorithm based on Preprocessing Techniques. IEEE, 2018, 186–191. DOI: 10.1109/ICACCCN.2018.8748429.
- [5] C. Bunkhumpornpat, K. Sinapiromsaran, and C. Lursinsap. Safe-Level-SMOTE: Safe-Level-Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling TEchnique for Handling the Class Imbalanced Problem. 2009, 475–482. DOI: 10.1007/978- 3-642-01307-2_43.
- [6] A. Ali, S. M. Shamsuddin, and A. L. Ralescu, (2015) “Classification with class imbalance problem: A review" International Journal of Advances in Soft Computing and its Applications 7(3): 176–204.
- [7] D. Devi, S. K. Biswas, and B. Purkayastha. “A Review on Solution to Class Imbalance Problem: Undersampling Approaches”. In: IEEE, 2020, 626–631.
- [8] G. Haixiang, L. Yijing, J. Shang, G. Mingyun, H. Yuanyue, and G. Bing, (2017) “Learning from classimbalanced data: Review of methods and applications" Expert Systems with Applications 73: 220–239. DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.12.035.
- [9] W.-C. Lin, C.-F. Tsai, Y.-H. Hu, and J.-S. Jhang, (2017) “Clustering-based undersampling in class-imbalanced data" Information Sciences 409-410: 17–26.
- [10] F. Rayhan, S. Ahmed, A. Mahbub, R. Jani, S. Shatabda, and D. M. Farid. “CUSBoost: ClusterBased Under-Sampling with Boosting for Imbalanced Classification”. In: IEEE, 2017, 1–5. DOI: 10.1109/CSITSS.2017.8447534.
- [11] V. Pratap and A. P. Singh, (2023) “Novel fuzzy clustering-based undersampling framework for class imbalance problem" International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management 14: 967–976. DOI: 10.1007/s13198-023-01897-1.
- [12] B. Das, N. C. Krishnan, and D. J. Cook. “Handling Imbalanced and Overlapping Classes in Smart Environments Prompting Dataset”. In: 2014, 199–219.
- [13] M. M. Rahman and D. N. Davis. “Cluster based under-sampling for unbalanced cardiovascular data”. In: 3 LNECS. 2013.
- [14] A. Rodriguez and A. Laio, (2014) “Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks" Science 344: 1492–1496. DOI: 10.1126/science.1242072.
- [15] S.-J. Yen and Y.-S. Lee, (2009) “Cluster-based undersampling approaches for imbalanced data distributions" Expert Systems with Applications 36: 5718–5727. DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2008.06.108.
- [16] P. Vuttipittayamongkol, E. Elyan, A. Petrovski, and C. Jayne. “Overlap-Based Undersampling for Improving Imbalanced Data Classification”. In: 2018, 689– 697. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-03493-1_72.
- [17] Y. Liu, Y. Liu, B. X. Yu, S. Zhong, and Z. Hu, (2023) “Noise-robust oversampling for imbalanced data classification" Pattern Recognition 133: 109008. DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.109008.
- [18] N. Lunardon, G. Menardi, and N. Torelli, (2014) “ROSE: a Package for Binary Imbalanced Learning" The R Journal 6: 79. DOI: 10.32614/RJ-2014-008.
- [19] J. A. Hartigan and M. A. Wong, (1979) “Algorithm AS 136: A K-Means Clustering Algorithm" Applied Statistics 28: 100. DOI: 10.2307/2346830.
- [20] N. V. Chawla, K. W. Bowyer, L. O. Hall, and W. P. Kegelmeyer, (2002) “SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique" Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 16: 321–357. DOI: 10.1613/jair.953.
- [21] H. Han, W.-Y. Wang, and B.-H. Mao. “BorderlineSMOTE: A New Over-Sampling Method in Imbalanced Data Sets Learning”. In: 2005, 878–887.
- [22] H. He, Y. Bai, E. A. Garcia, and S. Li. “ADASYN: Adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning”. In: IEEE, 2008, 1322–1328.
- [23] S. Barua, M. M. Islam, X. Yao, and K. Murase, (2014) “MWMOTE–Majority Weighted Minority Oversampling Technique for Imbalanced Data Set Learning" IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 26: 405–425. DOI: 10.1109/TKDE.2012.232.
- [24] D. L. Wilson, (1972) “Asymptotic Properties of Nearest Neighbor Rules Using Edited Data" IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics SMC-2: 408–421.
- [25] M. Kubat and S. Matwin. “Addressing the curse of imbalanced training sets: one-sided selectio”. In: 1997.
- [26] P. Hart, (1968) “The condensed nearest neighbor rule (Corresp.)" IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 14: 515–516. DOI: 10.1109/TIT.1968.1054155.
- [27] G. E. A. P. A. Batista, R. C. Prati, and M. C. Monard, (2004) “A study of the behavior of several methods for balancing machine learning training data" ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter 6: 20–29. DOI: 10.1145/1007730.1007735.
- [28] M. Koziarski. “CSMOUTE: Combined Synthetic Oversampling and Undersampling Technique for Imbalanced Data Classification”. In: IEEE, 2021, 1–8.
- [29] K. Veropoulos, C. Campbell, N. Cristianini, et al., (1999) “Controlling the sensitivity of support vector machines" Proceedings of the international joint conference on artificial intelligence:
- [30] R. Barandela, J. Sánchez, V. Garcıa, and E. Rangel, (2003) “Strategies for learning in class imbalance problems" Pattern Recognition 36: 849–851.
- [31] C. Drummond, R. C. Holte, et al. “C4. 5, class imbalance, and cost sensitivity: why under-sampling beats over-sampling”. In: 11. 2003.
- [32] S. Kotsiantis, D. Kanellopoulos, and P. Pintelas, (2006) “Handling imbalanced datasets : A review" Science 30:
- [33] Y. Sun, M. S. Kamel, A. K. Wong, and Y. Wang, (2007) “Cost-sensitive boosting for classification of imbalanced data" Pattern Recognition 40: 3358–3378.
- [34] K. L. Chong, Y. F. Huang, C. H. Koo, M. Sherif, A. N. Ahmed, and A. El-Shafie, (2023) “Investigation of crossentropy-based streamflow forecasting through an efficient interpretable automated search process" Applied Water Science 13: 6. DOI: 10.1007/s13201-022-01790-5.
- [35] Y. Freund and R. E. Schapire, (1996) “Experiments with a New Boosting Algorithm" Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Machine Learning:
- [36] X. Guo, Y. Yin, C. Dong, G. Yang, and G. Zhou. “On the Class Imbalance Problem”. In: IEEE, 2008, 192–201. DOI: 10.1109/ICNC.2008.871.
- [37] S. Wang and X. Yao. “Diversity analysis on imbalanced data sets by using ensemble models”. In: IEEE, 2009, 324–331. DOI: 10.1109/CIDM.2009.4938667.
- [38] N. V. Chawla, A. Lazarevic, L. O. Hall, and K. W. Bowyer. “SMOTEBoost: Improving Prediction of the Minority Class in Boosting”. In: 2003, 107–119.
- [39] C. Seiffert, T. M. Khoshgoftaar, J. V. Hulse, and A. Napolitano, (2010) “RUSBoost: A Hybrid Approach to Alleviating Class Imbalance" IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics - Part A: Systems and Humans 40: 185–197.
- [40] H. Hartono, O. S. Sitompul, T. Tulus, and E. B. Nababan, (2018) “Biased support vector machine and weightedsmote in handling class imbalance problem" International Journal of Advances in Intelligent Informatics 4: 21. DOI: 10.26555/ijain.v4i1.146.
- [41] S. Ahmed, F. Rayhan, A. Mahbub, M. R. Jani, S. Shatabda, and D. M. Farid. “LIUBoost: Locality Informed Under-Boosting for Imbalanced Data Classification”. In: 2019, 133–144. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-13- 1498-8_12.
- [42] D. Chen, X.-J. Wang, C. Zhou, and B. Wang, (2019) “The Distance-Based Balancing Ensemble Method for Data With a High Imbalance Ratio" IEEE Access 7: 68940–68956.
- [43] N. AlDahoul, A. N. Ahmed, M. F. Allawi, M. Sherif, A. Sefelnasr, K.-w. Chau, and A. El-Shafie, (2022) “A comparison of machine learning models for suspended sediment load classification" Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics 16: 1211–1232. DOI: 10.1080/19942060.2022.2073565.
- [44] M. Galar, A. Fernandez, E. Barrenechea, H. Bustince, and F. Herrera, (2012) “A Review on Ensembles for the Class Imbalance Problem: Bagging-, Boosting-, and Hybrid-Based Approaches" IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews) 42: 463–484. DOI: 10.1109/TSMCC.2011.2161285.
- [45] N. Matloff. The art of R programming: A tour of statistical software design. No Starch Press, 2011.
- [46] E. Elyan and M. M. Gaber, (2016) “A fine-grained Random Forests using class decomposition: an application to medical diagnosis" Neural Computing and Applications 27: 2279–2288.
- [47] J. Derrac, S. Garcia, L. Sanchez, and F. Herrera, (2015) “Keel data-mining software tool: Data set repository, integration of algorithms and experimental analysis framework" J. Mult. Valued Log. Soft Comput 17: 255–287