REFERENCES
- [1] Leou, R. C. (2011) Amulti-yeartransmissionplanning under a deregulated market. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst 33(3), 708–714. doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2010. 11.020
- [2] Dominguez, A. H., L. H. Macedo, A. H. Escobar, and R. Romero (2017) Multistage security-constrained HVAC/HVDC transmission expansion planning with a reduced search space. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 32(6), 4805–4817. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2017.2669323
- [3] Tejada, D. J., M. López-Lezama, M. J. Rider, and G. Vinasco (2015) Transmission network expansion planning considering repowering and reconfiguration. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 69, 213–221. doi: 10. 1016/j.ijepes.2015.01.008
- [4] Wu, Z., P. L. Zeng, X. P. Zhang, H. Fu, and Q. Dai (2015) Two-stage stochastic dual dynamic programming for transmission expansion planning with significant renewable generation, IET International Conference on Resilience of Transmission and Distribution Networks (RTDN), 1–6. doi: 10.1049/cp.2015.0881
- [5] Kim, H., S. Lee, S. Han, W. Kim, K. Ok, and S. Cho (2015) Integrated generation and transmission expansion planning using generalized Bender’s decomposition method, 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence Communication Technology, 493–497. doi: 10.1109/CICT.2015.29
- [6] Rahmani, M., G. Vinasco, M. J. Rider, R. Romero, and P. M. Pardalos (2014) Multistage transmission expansion planning considering fixed series compensation allocation, 2014 IEEE PES General Meeting | Conference Exposition, 1–1. doi: 10.1109/PESGM.2014. 6938959
- [7] Gallego, L. A., L. P. Garcés, M. Rahmani, and R. A. Romero (2017) High-performance hybrid genetic algorithm to solve transmission network expansion planning. Transm. Distrib. IET Gener. 11(5), 1111–1118. doi: 10.1049/iet-gtd.2016.0511
- [8] Silva, E. L. D., J. M. A. Ortiz, G. C. D. Oliveira, and S. Binato (2001) Transmission network expansion planning under a Tabu search approach. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 16 (1), 62–68. doi: 10.1109/59.910782
- [9] Cortes-Carmona, M., R. Palma-Behnke, and O. Moya (2009) Transmission network expansion planning by a hybrid simulated annealing algorithm, 2009 15th International Conference on Intelligent System Applications to Power Systems, 1–7. doi: 10.1109/ISAP.2009. 5352951
- [10] Hejeejo, R., and J. Qiu (2017) Probabilistic transmission expansion planning considering distributed generation and demand response programs, IET Renew Power Gener. 11(5), 650–658. doi: 10.1049/iet-rpg. 2016.0725
- [11] Molina, J. D., and H. Rudnick (2010) Transmission of electric energy: a bibliographic review, IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 8(3), 245–258. doi: 10.1109/TLA.2010.5538399
- [12] Hemmati, R., R. A. Hooshmand, and A. Khodabakhshian (2013) State-of-the-art of transmission expansion planning: comprehensive review, Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 23, 312–319. doi: 10.1016/j. rser.2013.03.015
- [13] Latorre, G., R. D. Cruz, J. M. Areiza, and A. Villegas (2003) Classification of publications and models on transmission expansion planning. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 18(2), 938–946. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2003. 811168
- [14] Rider, M. J., A. V. Garcia, and R. Romero (2007) Power system transmission network expansion planning using AC model, Transm. Distrib. IET Gener. 1(5), 731–742. doi: 10.1049/iet-gtd:20060465
- [15] Lin, W., W. Lei, G. Tian, and Y. Zhang (2018) MTLBO: a multi-objective multi-course teachinglearning-based optimization algorithm, Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 21(3), 331–342. doi: 10.6180/jase.201809_21(3).0004
- [16] Lin, W., L. Wang, Y. Zhang and C. Zhang (2018) Fullactive scheduling in job shop problems using an improved genetic algorithm, Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 21(4), 507–518.
- [17] Garver, L. L. (1970) Transmission network estimation using linear programming, IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 89(7), 1688–1697. doi: 10.1109/TPAS.1970. 292825
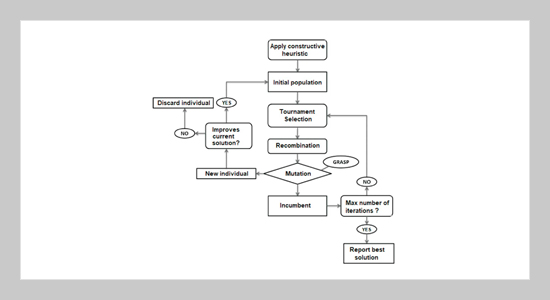
- [18] Rider, M. J., A. V. Garcia, and R. Romero (2004) A constructive heuristic algorithm to short term transmission network expansion planning,Proc.2004 IEEE Power Eng. Soc. Gen. Meet., Denver, USA, 2, 2108– 2114. doi: 10.1109/PES.2004.1373255
- [19] López-López, A. (2017) Planeamiento de la expansión de la red de transmisión considerando repotenciación, reconfiguración de circuitos existentes y ubicación de compensaciones en serie y en derivación, Universidad de Antioquia.
- [20] Rider, M. J. and A. V. Garcia (2004) A constructive heuristic algorithm to short term transmission network expansion planning, IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, 2107�2113. doi: 10.1109/PES.2004. 1373255