Lingwei Xu This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1, Hao Zhang2,3, Jingjing Wang1 and T. Aaron Gulliver3
1College of Information Science and Technology, Qingdao University of Science & Technology, Qingdao 266061, P.R. China
2College of Information Science and Engineering, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, P.R. China
3Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Victoria, Victoria V8W 2Y2, Canada
REFERENCES
- [1] Mumtaz, S., Huq, K. M. S. and Rodriguez, J., “Direct Mobile-to-mobile Communication: Paradigm for 5 G,” IEEE Wireless Communications, Vol. 21, No. 5, pp. 14�23 (2014). doi: 10.1109/MWC.2014.6940429
- [2] Seyfi, M., Muhaidat, S., Liang, J. and Uysal, M., “Relay Selection in Dual-Hop Vehicular Networks,” IEEE Signal Processing Letters, Vol. 18, No. 2, pp. 134�137 (2011). doi: 10.1109/LSP.2010.2102017
- [3] Gong, F. K., Ge, J. and Zhang, N., “SER Analysis of the Mobile-Relay-Based M2M Communication over Double Nakagami-m Fading Channels,” IEEE Communications Letters, Vol. 15, No.1, pp. 34�36 (2011). doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2010.111910.101683
- [4] Karagiannidis, G. K., Sagias, N. C. and Mathiopoulos, P. T., “N*Nakagami: a Novel Stochastic Model for Cascaded Fading Channels,” IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. 55, No. 8, pp. 1453�1458 (2007). doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2007.902497
- [5] Ilhan, H., Uysal, M. and Altunbas, I., “Cooperative Diversity for Intervehicular Communication: Performance Analysis and Optimization,” IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, Vol. 58, No. 7, pp. 3301�3310 (2009). doi: 10.1109/TVT.2009.2014685
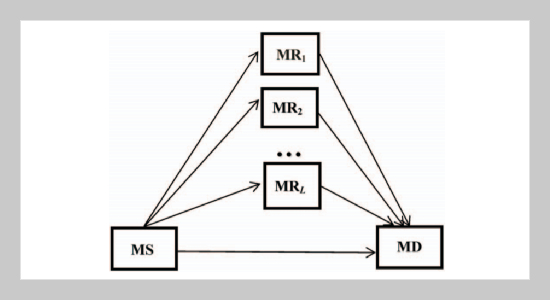
- [6] Xu, L. W., Zhang, H., Lu, T. T., Liu, X. and Wei, Z. Q., “Performance Analysis of the Mobile-Relay-Based M2M Communication over N-Nakagami Fading Channels,” Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, Vol. 18, No. 3, pp. 309�314 (2015). doi: 10.6180/jase. 2015.18.3.12
- [7] Xu, L. W., Zhang, H. and Gulliver, T. A., “Performance Analysis of IDF Relaying M2M Cooperative Networks over N-Nakagami Fading Channels,” KSII Transactions on Internet & Information Systems, Vol. 9, No. 10, pp. 3983�4001 (2015). doi: 10.3837/tiis. 2015.10.012
- [8] Xu, L. W., Zhang, H., Liu, X. and Gulliver, T. A., “Performance Analysis of FAF Relaying M2M Cooperative Networks over N-Nakagami Fading Channels,” International Journal of Signal Processing, Image Processing and Pattern Recognition, Vol. 8, No. 5, pp. 249�258 (2015). doi: 10.14257/ijsip.2015.8.5.26
- [9] Ochiai, H., Mitran, P. and Tarokh, V., “Variable-Rate Two-Phase Collaborative Communication Protocols for Wireless Networks,” IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, Vol. 52, No. 9, pp. 4299�4313 (2006). doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.880055
- [10] Yilmaz, F. and Kucur, O., “Exact Performance of Wireless Multihop Transmission for M-ary Coherent Modulations over Generalized Gamma Fading Channels,” International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, Cannes, France, pp. 1�5 (2008). doi: 10.1109/PIMRC.2008.4699662