Jian-Hua Tong1, Chin-Lung Chiu2 and Shu-Tao Liao This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.3 1Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering, Hungkuang University, Taichung, Taiwan 400, R.O.C.
2Department of Civil Engineering, National Central University, Taoyuan, Taiwan 320, R.O.C.
3Department of Civil Engineering, Chung Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan 300, R.O.C.
Received:
November 18, 2012
Accepted:
January 21, 2013
Publication Date:
March 1, 2013
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2013.16.1.07
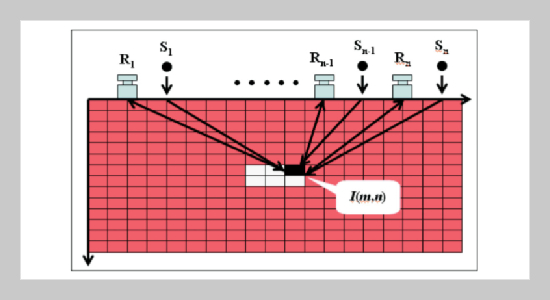
In this paper, a new elastic-wave-based NDT system was developed and then applied to reveal the defects in the concrete specimens by imaging method. This testing system integrates the point- source/point-receiver scheme with the synthetic aperture focusing technique (SAFT) to achieve the effect like scanning with a phase array system; hence it is equipped with large functioning depth because of the high-energy feature that transient elastic wave method possesses in comparison to traditional ultrasonic method. This NDT system is mainly composed of an impacting force generator, a displacement or velocity transducer, a signal capturing unit and operation software. To evaluate the feasibility of this system for scanning concrete structures, a concrete plate with embedded void was calibrated for experiment. Numerical simulations using 2D plane stress finite elements were performed for comparison purpose. Experimental results show good agreement with the numerical ones not only on the B-scan diagrams but also on the processed scanning images. It is concluded that the elastic- wave-based scanning system incorporated with SAFT scheme proposed in this paper exhibits high potential in inspecting the defects of in-situ concrete structures by imaging.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Nondestructive Test, Synthetic Aperture Focusing Technique, Elastic Stress Wave, Concrete Structure, Scanning Defect, Image Process
REFERENCES