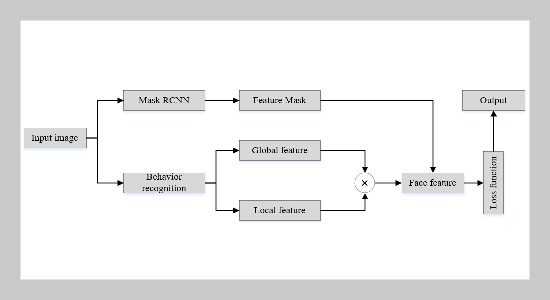
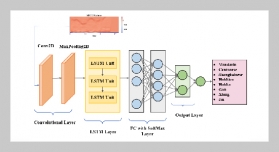
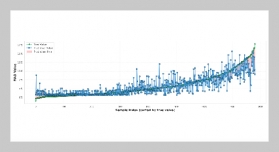
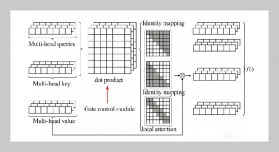
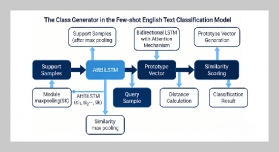
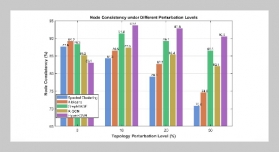
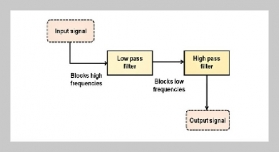
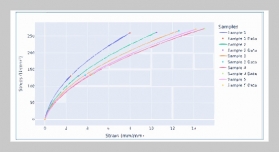
- [1] S. Yin, H. Li, L. Teng, A. A. Laghari, and V. V. Estrela, (2024) “Attribute-based multiparty searchable encryption model for privacy protection of text data" Multimedia Tools and Applications 83(15): 45881–45902. DOI: 10.1007/s11042-023-16818-4.
- [2] K. Chen, T. Yi, and Q. Lv, (2021) “Lightqnet: Lightweight deep face quality assessment for risk controlled face recognition" IEEE Signal Processing Letters 28: 1878–1882. DOI: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3109781.
- [3] J.M.Pimentel,R.C.Moioli, M.F.DeAraujo,andP.A. Vargas, (2023) “An Integrated Neurorobotics Model of the Cerebellar-Basal Ganglia Circuitry." International Journal of Neural Systems 33(11): DOI: 10.1142/S0129065723500594.
- [4] M. Besnassi, N. Neggaz, and A. Benyettou, (2020) “Face detection based on evolutionary Haar filter" Pat tern Analysis and Applications 23: 309–330. DOI: 10.1007/s10044-019-00784-5.
- [5] A. Singha, M. K. Bhowmik, and D. Bhattacherjee, (2020) “Akin-based Orthogonal Space (AOS): a subspace learning method for face recognition" Multimedia Tools and Applications 79(47): 35069–35091. DOI: 10.1007/s11042-020-08892-9.
- [6] Y. Feng, F. Wu, Q. Huang, X.-Y. Jing, Y. Ji, J. Yu, F. Chen, and L. Han. “Cross-modality multi-task deep metric learning for sketch face recognition”. In: 2019 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC). IEEE. 2019, 2277 2281. DOI: 10.1109/CAC48633.2019.8996397.
- [7] Y.Taigman,M.Yang,M.Ranzato,andL.Wolf.“Deep face: Closing the gap to human-level performance in face verification”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE. 2014, 1701–1708. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.220.
- [8] X. Wang and W. Zhang, (2021) “Anti-occlusion face recognition algorithm based on a deep convolutional neu ral network" Computers & Electrical Engineering 96: 107461. DOI: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2021.107461.
- [9] F. Schroff, D. Kalenichenko, and J. Philbin. “Facenet: Aunifiedembeddingforfacerecognition andcluster ing”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, 2015, 815–823. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298682.
- [10] M.Cheng, J. Bai, L. Li, Q. Chen, X. Zhou, H. Zhang, and P. Zhang. “Tiny-RetinaNet: a one-stage detec tor for real-time object detection”. In: Eleventh in ternational conference on graphics and image process ing (ICGIP 2019). 11373. SPIE. 2020, 195–202. DOI: 10.1117/12.2557264.
- [11] J. Deng, J. Guo, Y. Zhou, J. Yu, I. Kotsia, and S. Zafeiriou, (2019) “Retinaface: Single-stage dense face lo calisation in the wild" arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.00641:
- [12] J.-X. Tong, H. Li, and S.-L. Yin, (2020) “Research on face recognition method based on deep neural network" International Journal of Electronics and Informa tion Engineering 12(4): 182–188. DOI: 10.6636/IJEIE. 202012_12(4).05).
- [13] H. Zhang, J. Li, Y. Huang, and L. Zhang, (2013) “A nonlocal weighted joint sparse representation classifica tion method for hyperspectral imagery" IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 7(6): 2056–2065. DOI: 10.1109/ JSTARS.2013.2264720.
- [14] A.Creswell, T. White, V. Dumoulin, K. Arulkumaran, B. Sengupta, and A. A. Bharath, (2018) “Generative adversarial networks: An overview" IEEE signal pro cessing magazine 35(1): 53–65. DOI: 10.1109/MSP.2017.2765202.
- [15] H. Fan, H.-M. Hu, S. Liu, W. Lu, and S. Pu, (2020) “Correlation graph convolutional network for pedestrian attribute recognition" IEEE Transactions on Multime dia 24: 49–60. DOI: 10.1109/TMM.2020.3045286.
- [16] M.Zhu, D. Shi, M. Zheng, and M. Sadiq. “Robust fa cial landmark detection via occlusion-adaptive deep networks”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, 2019, 3486–3496. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00360.
- [17] X. Shao, Q. Wang, W. Yang, Y. Chen, Y. Xie, Y. Shen, and Z. Wang, (2021) “Multi-scale feature pyramid net work: A heavily occluded pedestrian detection network based on ResNet" Sensors 21(5): 1820. DOI: 10.3390/s21051820.
- [18] X. Wu and L. Zhao, (2019) “Study on iris segmenta tion algorithm based on dense U-Net" IEEE Access 7: 123959–123968. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2938809.
- [19] Y.Qu,R.K.Baghbaderani,H.Qi,andC.Kwan,(2020) “Unsupervised pansharpening based on self-attention mechanism" IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 59(4): 3192–3208. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3009207.
- [20] A. Boragule, H. Akram, J. Kim, and M. Jeon, (2022) “Learning to resolve uncertainties for large-scale face recog nition" Pattern Recognition Letters 160: 58–65. DOI: 10.1016/j.patrec.2022.06.004.
- [21] F. Boutros, N. Damer, M. Fang, F. Kirchbuchner, and A. Kuijper. “MixFaceNets: Extremely Efficient Face Recognition Networks”. In: 2021 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB). IEEE, 2021. DOI: 10.1109/IJCB52358.2021.9484374.
- [22] F. Ye, M. Ding, E. Gong, X. Zhao, and L. Hang. “Tiny face detection based on deep learning”. In: 2019 14th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Appli cations (ICIEA). IEEE. 2019, 407–412. DOI: 10.1109/ICIEA.2019.8834282.
- [23] M. Kim, A. K. Jain, and X. Liu. “Adaface: Quality adaptive margin for face recognition”. In: Proceed ings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2022, 18750–18759. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01819.
- [24] F. Boutros, N. Damer, F. Kirchbuchner, and A. Kui jper. “Elasticface: Elastic margin loss for deep face recognition”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF confer ence on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2022, 1578–1587. DOI: 10.1109/CVPRW56347.2022.00164.
- [25] T. Gong, X. Liu, and H. Yuan, (2022) “Face Recogni tion Method based on Feature Fusion and Convolutional Neural Network" International Core Journal of Engi neering 8(5): 526–537. DOI: 10.6919/ICJE.202205_8(5).0068.