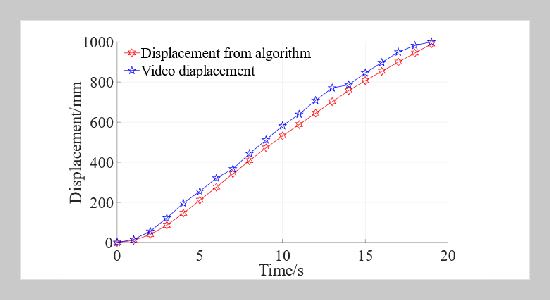
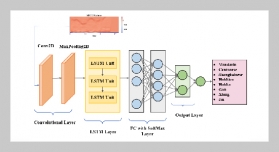
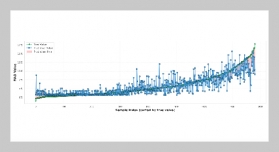
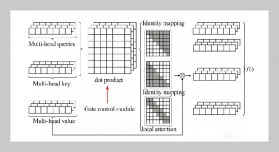
- [1] R. A. Mangushev, A. I. Osokin, and L. V. Garnyk, (2016) “Experience in preserving adjacent buildings dur�ing excavation of large foundation pits under conditions of dense development" Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering 53(5): 291–297. DOI: 10.1007/s11204-016-9401-9.
- [2] P. Lin, P. Liu, G. Ankit, and Y. J. Singh, (2021) “De�formation monitoring analysis and numerical simulation in a deep foundation pit" Soil Mechanics and Founda�tion Engineering 58(1): 56–62. DOI: 10.1007/s11204-021-09706-2.
- [3] K. Ganjalipour, (2021) “Review of inclinometer errors and provide correction methods for bias shift error and depth position error of the probe" Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 39(6): 4017–4034. DOI: 10.1007/s10706-021-01743-w.
- [4] E. S. Okiemute, M. N. Ono, and O. F. Oduyebo, (2018) “Comparative analysis of DGPS and total station accu�racies for static deformation monitoring of engineering structures" Journal of Environmental Science, Toxi�cology and Food Technology 12(6): 19–29.
- [5] J. G. Zhou, H. J. Xiao, W. W. Jiang, W. F. Bai, and G. L. Liu, (2019) “Automatic subway tunnel displacement mon�itoring using robotic total station" Measurement 2020: 15. DOI: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.107251.
- [6] H. Zhang, S. Xu, and T. Lu. “GPS height application and gross error detection in foundation pit monitor�ing”. In: Geotechnical Aspects of Underground Construc�tion in Soft Ground: Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium (IS-Shanghai), Shanghai-China, April-2008 (Vol-20). 2008, 239–242.
- [7] L. Hu, Y. Zhang, H. Zhang, and S. Tian, (2014) “Secu�rity monitoring technology of foundation excavation hor�izontal displacement by rapid static GPS method" Con�struction Technology 43(16): 56–58.
- [8] Z. X. Liu and X. J. Zhang, (2013) “Research on deforma�tion monitoring on supporting structure of deep founda�tion pit engineering based on gps" Applied Mechanics and Materials 239-240: 595–598. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.239-240.595.
- [9] B. Wolfgang and M. Andreas. “Investigating laser scanner accuracy”. In: Proceedings of Xixth Cipa Sym�posium. 10. 2003, 696–702.
- [10] X. L. Deng and L. H. Li, (2017) “Refined modeling of complex geological body based on three-dimensional laser scanning technique" Journal of Engineering Geology 25(01): 209–214. DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017.01.027.
- [11] D. Han, G. Qin, Y. Zhou, D. Wang, and Y. Yang, (2019) “Application of BIM and 3D laser scanning in foundation pit monitoring" Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong Uni�versity (Natural Science) 38(06): 72. DOI: 10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103706.
- [12] R. Bernini, A. Minardo, and L. Zeni, (2011) “Dis�tributed sensing at centimeter-scale spatial resolution by BOFDA: Measurements and signal processing" IEEE Photonics Journal 4(1): 48–56. DOI: 10.1109/JPHOT.2011.2179024.
- [13] C. Zhu, K. Zhang, H. Cai, Z. Tao, B. An, M. He, and J. Liu, (2019) “Combined application of optical fibers and CRLD bolts to monitor deformation of a pit-in-pit founda�tion" Advances in Civil Engineering 2019(1): 1–16. DOI: 10.1155/2019/2572034.
- [14] J. Wu, L. Peng, J. Li, X. Zhou, J. Zhong, C. Wang, and J. Sun, (2021) “Rapid safety monitoring and analysis of foundation pit construction using unmanned aerial vehi�cle images" Automation in Construction 128: 103706. DOI: 10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103706.
- [15] L. Wang, X. Weng, Y. Li, B. Guan, Z. Yao, and Q. Bo, (2018) “Study on the application of ultrasonic wave in foundation settlement monitoring" Geotechnical Test�ing Journal 42(2): 365–384.
- [16] L. L. Guan, S. H. Zhang, Y. H. Li, and P. Sun, (2015) “Application of dense surface modeling technology in dis�placement monitoring of deep foundation pit" Yangtze River 46(11): 76–79.
- [17] S. Alatza, I. Papoutsis, D. Paradissis, C. Kontoes, and G. A. Papadopoulos, (2020) “Multi-temporal in SAR analysis for monitoring ground deformation in Amor�gos Island, Greece" Sensors 20(2): 338. DOI: 10.3390/s20020338.
- [18] L. Yang, T. Wu, and S. Kang, (2002) “The microsensor technology using to identify the initiation time of impact induced elastic waves" Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 5(3): 121–127. DOI: 10.6180/jase. 2002.5.3.01.
- [19] V. Bennett, T. Abdoun, and M. Barendse, (2015) “Eval�uation of soft clay field consolidation using MEMS-based in-place inclinometer-accelerometer array" Geotechnical Testing Journal 38(3): 290–302.
- [20] C. Li, S. W. Song, and J. Z. Sun, (2023) “Application and simulation research of MEMS inertial sensor in reservoir bank slope deformation monitoring" Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 42(05): 1248–1258.
- [21] D. W. Ha, J. M. Kim, and Y. Kim, (2018) “Develop�ment and application of a wireless MEMS-based borehole inclinometer for automated measurement of ground move�ment" Automation in Construction 87: 49–59. DOI: 10.1016/j.autcon.2017.12.011.
- [22] M. Darrow and D. Jensen, (2014) “Cold region applica�tions for in-place inclinometers based on microelectrome�chanical systems technology: Four evaluation case stud�ies" Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board 2433(1): 1–9. DOI: 10.3141/2433-01.
- [23] T. Abdoun, P. Bennett, L. Danisch, and M. Barendse. “Real-time construction monitoring with a wireless shape-acceleration array system”. In: Geotechnical Spe�cial Publication. 17. 09. 2008, 533–540. DOI: 10.1061/40972(311)67.
- [24] M. Barzegar, S. Blanks, B. Sainsbury, and W. Timms, (2022) “MEMS technology and applications in geotechni�cal monitoring: A review" Measurement Science and Technology 33(5): 052001. DOI: 10.1088/1361-6501/ac4f00.
- [25] S. Stiros, (2008) “Errors in velocities and displacements deduced from accelerographs: An approach based on the theory of error propagation" Soil Dynamics and Earth�quake Engineering 28(5): 415–420. DOI: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2007.07.004.
- [26] A. Brandt and R. Brincker, (2014) “Integrating time signals in frequency domain – comparison with time do�main integration" Measurement 58: 511–519. DOI: 10.1016/j.measurement.2014.09.004.
- [27] L. Zhu, Y. Fu, R. Chow, B. F. Spencer, J. W. Park, and K. Mechitov, (2018) “Development of a high-sensitivity wireless accelerometer for structural health monitoring" Sensors 18(1): 262. DOI: 10.3390/s18010262.
- [28] C. Yang, D. W. Tao, Q. Ma, Q. C. Jie, and L. Y. Wang, (2019) “Realization of strong earthquake data processing technology based on Matlab" seismological and geo�magnetic observation and research 40(03): 148–153.
- [29] H. Zhu, K. Gao, Y. Xia, F. Gao, S. Weng, Y. Sun, and Q. Hu, (2020) “Multi-rate data fusion for dynamic displacement measurement of beam-like supertall struc�tures using acceleration and strain sensors" Structural Health Monitoring 19(2): 520–536. DOI: 10.1177/1475921719857043.
- [30] V. Vukmirica, I. Trajkovski, and N. Asanovic, (2012) “Two methods for the determination of inertial sensor pa�rameters" Scientific Technical Review 60(3): 27–33.
- [31] X. Cheng, T. Zhou, F. Sun K.and Yang, H. Xie, and S. Wang, (2019) “Time/Frequency-domain integration method of vibration acceleration signal processed by wavelet denoising" Electric power and energy 40(06): 633–637.
- [32] P. Hsieh and C. Ou, (1999) “Shape of ground sur�face settlement profiles caused by excavation" Canadian Geotechnical Journal 35(6): 1004–1017. DOI: 10.1139/t98-056.