REFERENCES
- [1] H. T. Nguyen, P. H. Duong, and E. Cambria, (2019) “Learning short-text semantic similarity with word embeddings and external knowledge sources" Knowledge-Based Systems 182: 104842. DOI: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.07.013.
- [2] K. Papineni, S. Roukos, T. Ward, and W.-J. Zhu. “BLEU: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation”. In: Proceedings of the 40th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. 2002, 311–318.
- [3] W. Yin and H. Schütze. “Convolutional neural network for paraphrase identification”. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. 2015, 901–911. DOI: 10.3115/v1/n15-1091.
- [4] M. Mohler, R. Bunescu, and R. Mihalcea. “Learning to grade short answer questions using semantic similarity measures and dependency graph alignments”. In: Proceedings of the 49th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics: Human language technologies. 2011, 752–762.
- [5] S. Minaee, N. Kalchbrenner, E. Cambria, N. Nikzad, M. Chenaghlu, and J. Gao, (2020) “Deep learning based text classification: A comprehensive review" arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.03705:
- [6] B. Sriram, D. Fuhry, E. Demir, H. Ferhatosmanoglu, and M. Demirbas. “Short text classification in twitter to improve information filtering”. In: Proceedings of the 33rd international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval. 2010, 841–842. DOI: 10.1145/1835449.1835643.
- [7] S. Poria, I. Chaturvedi, E. Cambria, and F. Bisio. “Sentic LDA: Improving on LDA with semantic similarity for aspect-based sentiment analysis”. In: 2016 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN). IEEE. 2016, 4465–4473. DOI: 10.1109/IJCNN.2016.7727784.
- [8] Y. Kim, (2014) “Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification" arXiv preprint arXiv:1408.5882:DOI: 10.3115/v1/d14-1181.
- [9] J. L. Elman, (1990) “Finding structure in time" Cognitive science 14(2): 179–211. DOI: 10 . 1016/0364 -0213(90)90002-E.
- [10] S. Hochreiter and J. Schmidhuber, (1997) “Long shortterm memory" Neural computation 9(8): 1735–1780.
- [11] K. Cho, B. Van Merriënboer, C. Gulcehre, D. Bahdanau, F. Bougares, H. Schwenk, and Y. Bengio, (2014) “Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation" arXiv preprint arXiv:1406.1078: DOI: 10 . 3115 / v1 / d14 -1179.
- [12] J. Bromley, I. Guyon, Y. LeCun, E. Säckinger, and R. Shah. “Signature verification using a" siamese" time delay neural network”. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. 1994, 737–744.
- [13] J. Mueller and A. Thyagarajan. “Siamese recurrent architectures for learning sentence similarity”. In: thirtieth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence. 2016.
- [14] P. Neculoiu, M. Versteegh, and M. Rotaru. “Learning text similarity with siamese recurrent networks”. In: Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Representation Learning for NLP. 2016, 148–157.
- [15] W. Yin, H. Schütze, B. Xiang, and B. Zhou, (2016) “Abcnn: Attention-based convolutional neural network for modeling sentence pairs" Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics 4: 259–272.
- [16] T. Ranasinghe, C. Orasan, and R. Mitkov. “Semantic textual similarity with siamese neural networks”. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing (RANLP 2019). 2019, 1004–1011.
- [17] Z. Li, H. Lin, W. Zheng, M. M. Tadesse, Z. Yang, and J.Wang, (2020) “Interactive Self-Attentive Siamese Network for Biomedical Sentence Similarity" IEEE Access 8: 84093–84104. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2985685.
- [18] Q. Chen, X. Zhu, Z. Ling, S. Wei, H. Jiang, and D. Inkpen, (2016) “Enhanced lstm for natural language inference" arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.06038: DOI: 10.18653/v1/P17-1152.
- [19] Z. Wang, W. Hamza, and R. Florian, (2017) “Bilateral multi-perspective matching for natural language sentences" arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.03814:
- [20] N. Xie, S. Li, and J. Zhao. “ERCNN: Enhanced Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks for Learning Sentence Similarity”. In: China National Conference on Chinese Computational Linguistics. Springer. 2019, 119–130. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-32381-3_10.
- [21] Z. Li, H. Lin, C. Shen,W. Zheng, Z. Yang, and J.Wang, (2020) “Cross2Self-attentive Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Network with BERT for Biomedical Semantic Text Similarity": 1051–1054. DOI: 10 . 1109 / BIBM49941 . 2020.9313452.
- [22] D. Bahdanau, K. Cho, and Y. Bengio, (2014) “Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate" arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0473:
- [23] L. Mou, R. Men, G. Li, Y. Xu, L. Zhang, R. Yan, and Z. Jin, (2015) “Natural language inference by tree-based convolution and heuristic matching" arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.08422: DOI: 10.18653/v1/p16-2022.
- [24] A. Graves and J. Schmidhuber, (2005) “Framewise phoneme classification with bidirectional LSTM and other neural network architectures" Neural networks 18(5-6): 602–610. DOI: 10.1016/j.neunet.2005.06.042.
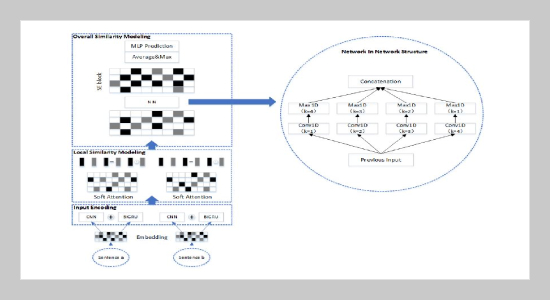
- [25] M. Lin, Q. Chen, and S. Yan, (2013) “Network in network" arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.4400:
- [26] K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun. “Deep residual learning for image recognition”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016, 770–778. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90.
- [27] J. Hu, L. Shen, and G. Sun. “Squeeze-and-excitation networks”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2018, 7132–7141. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745.
- [28] V. Nair and G. E. Hinton. “Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines”. In: ICML. 2010.
- [29] W. Dolan, C. Quirk, C. Brockett, and B. Dolan, (2004) “Unsupervised construction of large paraphrase corpora: Exploiting massively parallel news sources":
- [30] D. Cer, M. Diab, E. Agirre, I. Lopez-Gazpio, and L. Specia, (2017) “Semeval-2017 task 1: Semantic textual similarity-multilingual and cross-lingual focused evaluation" arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.00055:
- [31] C.-T. J. Huang. Logical relations in Chinese and the theory of grammar. Taylor & Francis, 1998.
- [32] X. Liu, Q. Chen, C. Deng, H. Zeng, J. Chen, D. Li, and B. Tang. “Lcqmc: A large-scale chinese question matching corpus”. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics. 2018, 1952–1962.
- [33] S. Li, Z. Zhao, R. Hu, W. Li, T. Liu, and X. Du, (2018) “Analogical reasoning on chinese morphological and semantic relations" arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.06504: DOI:10.18653/v1/p18-2023.
- [34] N. Srivastava, G. Hinton, A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, and R. Salakhutdinov, (2014) “Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting" The journal of machine learning research 15(1): 1929–1958.
- [35] D. P. Kingma and J. Ba, (2014) “Adam: A method for stochastic optimization" arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980:
- [36] G. S. Tomar, T. Duque, O. Täckström, J. Uszkoreit, and D. Das, (2017) “Neural paraphrase identification of questions with noisy pretraining" arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04565: