Yin-Tien Wang This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1, Duen-Yan Hung1 and Sheng-Hsien Cheng1 1Department of Mechanical and Electro-Mechanical Engineering, Tamkang University, Tamsui, Taiwan 251, R.O.C.
Received:
October 25, 2009
Accepted:
October 19, 2010
Publication Date:
June 1, 2011
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2011.14.2.05
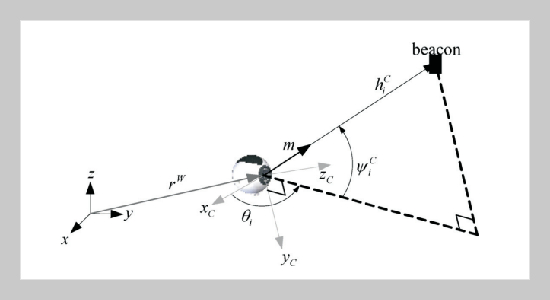
The paper presents a algorithm of visual simultaneous localization and mapping (vSLAM) for a small-size humanoid robot. The algorithm includes the procedures of image feature detection, good feature selection, image depth calculation, and feature state estimation. To ensure robust feature detection and tracking, the procedure is improved by utilizing the method of Speeded Up Robust Features (SURF). Meanwhile, the procedures of image depth calculation and state estimation are integrated in an extended Kalman filter (EKF) based estimation algorithm. All the computation schemes of the visual SLAM are implemented on a small-size humanoid robot with low-cost Window-based PC. Experimentation is performed and the results show that the performance of the proposed algorithm is efficient for robot visual SLAM in the environments.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Speeded Up Robust Features (SURF), Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM), Image Feature Initialization, Humanoid Robot
REFERENCES