REFERENCES
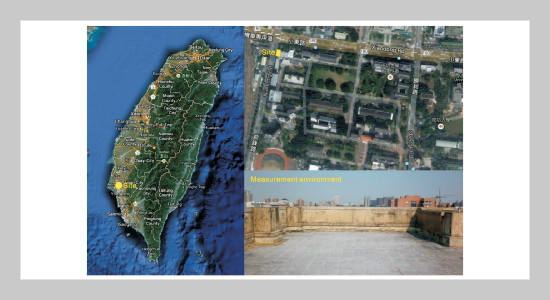
- [1] Jhang Jian, S. Y., A Fundamental Study on Heat Island Mitigation: The Influence of Thermo-physical Properties on Surface Temperature, Master Dissertation, IShou University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan (2009). doi: 10. 1002/j.1477-8696.1960.tb00659.x
- [2] Chandler, T. J., “Wind as a Factor of Urban Temperatures: A Survey in North-east London,” Weather, Vol. 15, pp. 204213 (2014). doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1989) 0702.0.CO;2
- [3] Thomas, R. K. and Philip, D. J., “Urban Biases in Areaaveraged Surface Air Temperature Trends,” American Meteorological Society, Vol. 70, pp. 265270 (1989).
- [4] Huang, Y. S., The Effect of Material Composition on Concrete Albedo, Master Dissertation, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan (2010).
- [5] Deng, W. Y., Effects of Albedo of Roof Insulation Materials on Surface Temperature, Master Dissertation, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan (2012).
- [6] Navigant Consulting Inc., “Building Technologies Program, Assessment of International Urban Heat Island Research - Literature Review of International Studies on Urban Heat Island Countermeasures,” Draft Report, USDOE, Washington, DC., U.S.A. (2011).
- [7] Akbari, H. and Damon Matthews, H., “Global Cooling Updates: Reflective Roofs and Pavements,” Energy and Build, Vol. 55, pp. 26 (2012). doi: 10.1016/j. enbuild.2012.02.055
- [8] Jo, J. H., Carlson, J. D., Golden, J. S. and Bryan, H., “An Integrated Empirical and Modeling Methodology for Analyzing Solar Reflective Roof Technologies on Commercial Buildings,” Building and Environment, Vol. 45, pp. 453460 (2010). doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv. 2009.07.001
- [9] Takashi, A. and Vu, T. A., “Characteristics of Permeable Pavement during Hot Summer Weather and Impact on the Thermal Environment,” Building and Environment, Vol. 35, pp. 363375 (2000). doi: 10.1016/ S0360-1323(99)00020-7
- [10] Santamouris, M., Gaitani, N., Spanou, A., Saliari, M., Giannopoulou, K. and Vasilakopoulou, K., “Using Cool Paving Materials to Improve Microclimate of Urban Areas Design Realization and Results of the Flisvos Project,” Building and Environment, Vol. 53, pp. 128 136 (2012). doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2012.01.022
- [11] Santamouris, M., “Cooling the Cities A Review of Reflective and Green Roof Mitigation Technologies to Fight Heat Island and Improve Comfort in Urban environments,” Solar Energy, Vol. 103, pp. 682703 (2012). doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2012.07.003
- [12] Synnefa, A., Karlessi, T., Gaitahi, N., Santamouris, M., Assimakopoulos, D. N. and Papakatsikas., “Experimental Testing of Cool Colored Thin Layer Asphalt and Estimation of its Potential to Improve the Urban Microclimate,” Building and Environment, Vol. 46, pp. 3844 (2011). doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2010. 06.014
- [13] Racine, T. A. and P., “Fabiana Lourenço Ferreira, Measurement of Albedo and Analysis of its Influence the Surface Temperature of Building Roof Materials,” Energy and Buildings, Vol. 37, pp. 295300 (2005). doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2004.03.009
- [14] Akbari, H., Levinson, R. and, Stern, S., “Procedure for Measuring the Solar Reflectance of Flat or Curved Roofing Assemblies,” Solar Energy, Vol. 82, pp. 648 655 (2008). doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2008.01.001
- [15] Simpson, J. R. and Mcpherson, E. G., “The Effects of Roof Albedo Modification on Cooling Loads of Scale Model Residences in Tucson, Arizona,” Energy and Buildings, Vol. 2, pp. 127137 (1997). doi: 10.1016/ S0378-7788(96)01002-X
- [16] David, J. S., Kyle, R. and Del, S., “Field Measurement of Albedo for Limited Extent Test Surfaces,” Solar Energy, Vol. 80, pp. 589599 (2006). doi: 10.1016/j. solener.2005.03.012