REFERENCES
- [1] Pan, T. C., Brownichu, J. M. W. and You, X. T., “Correlating Measured and Simulated Dynamic Response of a Tall Building to Long-Distance Earthquake,” Earthquake Engng Struct. Dyn., Vol. 33, pp. 611�632 (2004). doi: 10.1002/eqe.366
- [2] Brownjohn, J. M. W. and Pan, T. H., “Response of Tall Building to Weak Long Distance Earthquakes,” Earthquake Engng Struct. Dyn., Vol. 30, pp. 709�729 (2001). doi: 10.1002/eqe.32
- [3] Li, Q. S., Zhi, L. H., Tuan, Alex Y., Kao, C. S., Su, S. C. and Wu, C. F., “Dynamic Behavior of Taipei 101 Tower: Field Measurement and Numerical Analysis,” J Struct Eng-ASCE, Vol. 137, No. 1, pp. 143�155 (2011). doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0000264
- [4] Smith, R., Merello, R. and Willford, M., “Intrinsic and Supplementary Damping in Tall Buildings,” Proceedings of the ICE - Structures and Buildings, Vol. 163, No. 2, pp. 111�118 (2010). doi: 10.1680/stbu.2010. 163.2.111
- [5] Kareem, A. and Kijewski, T., “Mitigation of Motions of Tall Buildings with Specific Examples of Recent Applications,” Wind and Struct., Vol. 2, No. 3, pp. 201�251 (1999). doi: 10.12989/was.1999.2.3.201
- [6] Den Hartog, J. P., Mechanical Vibrations (4th edition), McGraw-Hill: New York (1956).
- [7] Chang, C. C, “Mass Dampers and Their Optimal Designs for Building Vibration Control,” Eng Struct., Vol. 21, No. 5, pp. 454�463 (1999). doi: 10.1016/ S0141-0296(97)00213-7
- [8] Sgobba, S. and Marano, G. C., “Optimum Design of Linear Tuned Mass Dampers for Structures with Nonlinear Behavior,” Mech Syst Signal Processing, Vol. 24, No. 6, pp. 1739�1755 (2010). doi: 10.1016/j. ymssp.2010.01.009
- [9] Leung, A. Y. T. and Zhang, H. J., “Particle Swarm Optimization of Tuned Mass Dampers,” Eng Struct., Vol. 31, No. 3, pp. 715�728 (2009). doi: 10.1016/j. engstruct.2008.11.017
- [10] Leung, A. Y. T., Zhang, H. J., Cheng, C. C. and Lee, Y. Y., “Particle Swarm Optimization of TMD by Non-- Stationary Base Excitation during Earthquake,” Earthq Eng & Struct D, Vol. 37, No. 9, pp. 1223�1246 (2008). doi: 10.1002/eqe.811
- [11] Lee, C. L., Chen, Y. T., Chung, L. L. and Wang, Y. P., “Optimal Design Theories and Applications of Tuned Mass Dampers,” Eng Struct., Vol. 28, No. 1, pp. 43�53 (2006). doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2005.06.023
- [12] Xu, Y. L., Kwok, K. C. S. and Samali, B., “Control of Wind-Induced Tall Building Vibration by Tuned Mass Dampers,” J Wind Eng Ing Aerodynaimcs, Vol. 40, No. 1, pp. 1�32 (1992). doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(92) 90518-F
- [13] Gerges, R. R. and Vickery, B. J., “Wind Tunnel Study of the Across-Wind Response of a Slender Tower with a Nonlinear Tuned Mass Damper,” J Wind Eng Ind Aerod, Vol. 91, No. 8, pp. 1069�1092 (2003). doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(03)00053-9
- [14] Rana, R. and Soong, T. T., “Parametric Study and Simplified Design of Tuned Mass Dampers,” Eng Struct., Vol. 20, No. 3, pp. 193�204 (1998). doi: 10.1016/ S0141-0296(97)00078-3
- [15] Warburton, G. B. and Ayorinde, E. O., “Optimum Absorber Parameters for Simple Systems,” Earthq Eng & Struct Dyn., Vol. 8, No. 3, pp. 197�217 (1980). doi: 10.1002/eqe.4290080302
- [16] Ayorinde, E. O. and Warburton, G. B., “Minimizing Structural Vibrations with Absorbers,” J. Earthq Eng & Struct Dyn., Vol. 8, No. 3, pp. 219�236 (1980). doi: 10.1002/eqe.4290080303
- [17] Warburton, G. B., “Optimum Absorber Parameters for Minimizing Vibration Response,” J Earthq Eng & Struct Dyn., Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 251�262 (1981). doi: 10.1002/eqe.4290090306
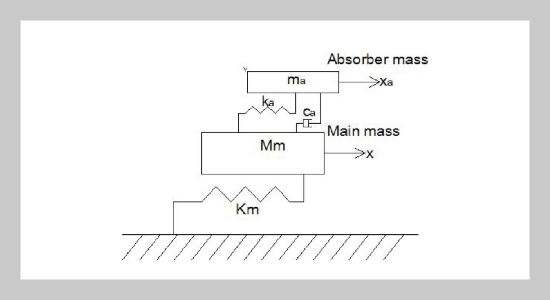
- [18] Research Institute of Building & Construction, Report on the Structural Design Scheme of Taipei 101, Ever Green Consulting Engineering, Inc, Taipei (1999).
- [19] Korenev, B. G. and Reznikov, L. M., Dynamic Vibration Absorbers Theory and Technical Applications, John Wiley & Sons Ltd (1993).
- [20] Wind-Induced Structural Responses Cladding Wind Load Study, Roman Williams Davies & Irwin Inc (RWDI) (1999).
- [21] Huang, S. H. and Li, Q. S., “Large Eddy Simulation of Wind Effects on a Supper-Tall Building,” Wind Struct., Vol. 13, pp. 557�580 (2010). doi: 10.12989/was. 2010.13.6.557
- [22] International Standards Organization Wind Load Committee, Proposal for Wind Loading Standard, ISO TC 98/SC3/WG2 (1987).