Sofiane Soulimane1, Arnaud Pouydebasque This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1, Sébastien Bolis1, Fabrice Jacquet1, Claudine Bridoux1, Florian Dupont1, Christophe Poulain1, Stéphane Moreau1 and Stephane Fanget1 1CEA, LETI, MINATEC Campus, F-38054 Grenoble, France
Received:
May 1, 2013
Accepted:
October 12, 2013
Publication Date:
March 1, 2014
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2014.17.1.02
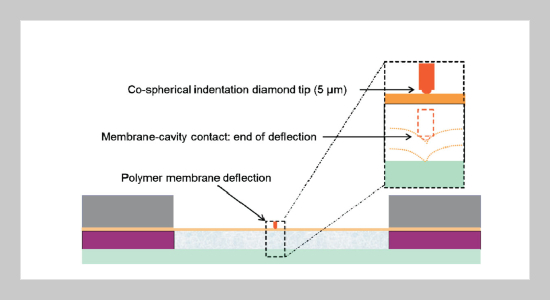
In this study, a novel methodology to assess the stiffness and evaluate the residual stress of thin, flexible polymer membranes is presented. This methodology is based on original test structures where the membrane is supported by a liquid in a circular cavity and uses stiffness measurement by point deflection with a nano-indenter. Knowing the Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio of the material and using the geometrical dimensions of the membrane (thickness and radius) the residual stress can be extracted from the stiffness values using an analytical model. Several polymers with different Young’s modulus, chemical composition, and thickness were evaluated using this method. Values of residual stress were extracted that are comparable to those obtained by the well-established Stoney method when this was applicable (i.e. relatively large residual stress) with a much lower uncertainty. Moreover, very low values of residual stress were measured with this method that could not be estimated reliably using the Stoney methodABSTRACT
Keywords:
Polymer Membrane, Residual Stress, Nano-Indenter, Membrane Flexion, Stiffness
REFERENCES