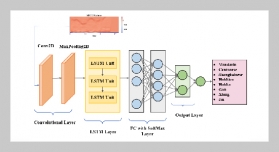
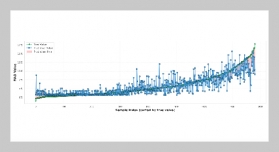
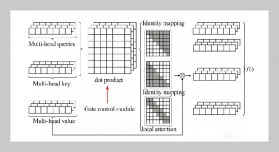
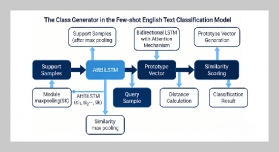
REFERENCES
- [1] Intelligent Robotics Industry: Analysis & Investment Opportunities, Department of Investment Services, Ministry of Economic Affairs, Taipei: Ministry of Economic Affairs (2008).
- [2] Jia, L. Q., Liu, H. M., Wang, Z. H. and Chen, H., “An Effective Non-HT Circle Detection for Centers and Radii,” Proc. of the 2011 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (ICMLC), Guilin, China, Vol. 10�13, pp. 814�818 (2011). doi: 10.1109/ ICMLC.2011.6016769
- [3] Ceccarelli, M., Petrosino, A. and Laccetti, G., “Circle Detection Based on Orientation Matching,” Proc. of 11th International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing, Palermo, Italy, Vol. 26�28, pp. 119�124 (2001). doi: 10.1109/ICIAP.2001.956995
- [4] Rad, A. A., Faez, K. and Qaragozlou, N., “Fast Circle Detection Using Gradient Pair Vectors,” DICTA, pp. 879�888 (2003).
- [5] Ho, C. T. and Chen L. H. “A Fast Ellipse/Circle Detector Using Geometric Symmetry,” Pattern Recognition, Vol. 28, Issue 1, pp. 117�124 (1995). doi: 10. 1016/0031-3203(94)00077-Y
- [6] Davies, E. R., Machine Vision: Theory, Algorithms, Practicalities, Academic Press, London (1990). doi: 10.1016/1049-9660(91)90080-9
- [7] Ballard, D. H. “Generalizing the Hough Transform to Detect Arbitrary Shapes,” Pattern Recognition, Vol. 13, No. 2, pp. 111�122 (1981). doi: 10.1016/0031- 3203(81)90009-1
- [8] Brown, C. M. “Inherent Bias and Noise in the Hough Transform,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol. 5, pp. 493�505 (1983). doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.1983.4767428
- [9] Illingworth, J. and Kittler, J., “Survey: A Survey of the Hough Transform,” Computer Vision, Graphics, Image Process, Vol. 44, Issue 1, pp. 87�116 (1988). doi: 10.1016/S0734-189X(88)80033-1
- [10] Leavers, V. F., “Survey: Which Hough Transform,” CVGIP: Image Understanding, Vol. 58, pp. 250�264 (1993). doi: 10.1006/cviu.1993.1043
- [11] Duda, R. O. and Hart, P. E., “Use of the Hough Transformation to Detect Lines and Curves in Pictures,” Communications of the ACM, Vol. 15, Issue 1, pp. 11�15 (1972). doi: 10.1145/361237.361242
- [12] Xu, L., Oja, E. and Kultanan, P., “A New Curve Detection Method: Randomized Hough Transform (RHT),” Pattern Recognition Letters, Vol. 11, Issue 5, pp. 331�338 (1990). doi: 10.1016/0167-8655(90)90042- Z
- [13] Xu, L. and Oja, E., “Randomized Hough Transform (RHT): Basic Mechanisms, Algorithms, and Computational Complexities,” CVGIP: Image Understanding, Vol. 57, No. 2, pp. 131�154 (1993). doi: 10.1006/ ciun.1993.1009
- [14] Chen, T. C. and Chung, K. L., “An Efficient Randomized Algorithm for Detecting Circles,” Computer Vision and Image Understanding, Vol. 83, No. 2, pp. 172�191 (2001). doi: 10.1006/cviu.2001.0923
- [15] D’Orazio, T., Guaragnella, C., Leo, M. and Distante, A., “A New Algorithm for Ball Recognition Using Circle Hough Transform and Neural Classifier,” Pattern Recognition, Vol. 37, No. 3, pp. 393�408 (2004). doi: 10.1016/S0031-3203(03)00228-0
- [16] Gonzalez, R. C. and Woods, R. E., Digital Image Processing 3/e, 3rd ed., Prentice Hall, United States (2008).
- [17] Yu, C. J., Hardware/Software Co-Design of Real-Time Human Face Detection, Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, Tamkang University, Taiwan (2010).
- [18] Chiu, C. C., Ku, M. Y. and Liang, L. W., “A Robust Object Segmentation System Using a ProbabilityBased Background Extraction Algorithm,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, Vol. 20, No. 4, pp. 518�528 (2010). doi: 10. 1109/TCSVT.2009.2035843
- [19] Xu, D., Liu, J., Li, X., Liu, Z. and Tang, X., “Insignificant Shadow Detection for Video Segmentation,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, Vol. 15, No. 8, pp. 1058�1064 (2005). doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2005.852402
- [20] Chung, K. L., Image Processing and Computer Vision, 5th ed., Tunghua, Taiwan (2008).
- [21] Lindeberg, T., “Edge Detection and Ridge Detection with Automatic Scale Selection,” International Journal of Computer Vision, Vol. 30, No. 2, pp. 117�156 (1998). doi: 10.1023/A:1008097225773
- [22] Canny, J., “A Computational Approach to Edge Detection,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol. 6, pp. 679�698 (1986). doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.1986.4767851
- [23] Sobel operator, Information on http://en.wikipedia. org/wiki/Sobel_operator
- [24] Pythagorean theorem, Information on http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pythagorean_theorem
- [25] Cramer’s rule, Information on http://en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/Cramer’s_rule