Chin-Tsan Wang This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1, Cheng Kuang Shaw2 and Tzu-Yang Hu1 1Department of Mechanical and Electromechanical Engineering, National I-Lan University, I-Lan, Taiwan 260, R.O.C.
2Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, University of California: Los Angeles
Received:
June 16, 2009
Accepted:
August 5, 2010
Publication Date:
March 1, 2011
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2011.14.1.04
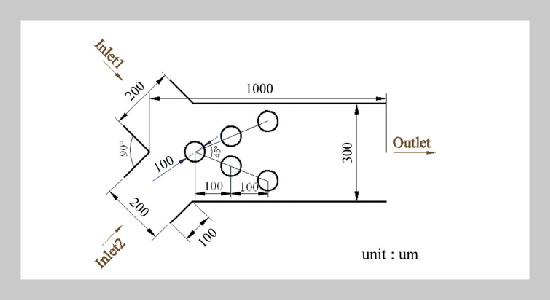
An important obstacle to overcome in the advancement of microbial fuel cell (MFC) technology is to improve the efficiency of the micro-channel and micro-mixer components in a MFC system. Through the use of a commercial computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulator, this project analyzed three passive Y-type micro-mixer designs and collected data pertaining to velocity, pressure drop, and performance flow efficiency. Various factors considered in this study include inlet aspect ratios and varying inlet Reynolds ratios. When the micro-mixers were investigated, the introduction of mixing cylinders inside the micro-mixer increases mixing efficiency but also raises the pressure drop. In addition, the flow mixing would be enhanced with a lower Aspect ratio and a larger inlet Reynolds ratio. The side wall effect and shear stress would offer a positive effect on flow mixing. The concept of the cylinders embedded in the flow channel would be applied to MFCs for improvement of power performance.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Passive Micro Mixer, Cylinder, Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC)
REFERENCES