1Department of Applied Mechanics Birla Institute of Technology Mesra, Ranchi- 835 215, India
2Department of Production Engineering Birla Institute of Technology Mesra, Ranchi- 835 215, India
Received:
May 23, 2003
Accepted:
September 25, 2003
Publication Date:
December 1, 2003
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2003.6.4.04
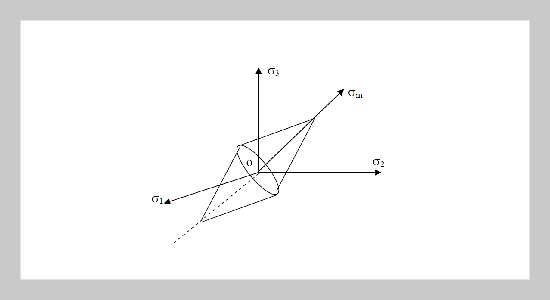
The paper reports on an investigation into the various aspects of closed die cold forging of polygonal powder preforms, which have been compacted and sintered from atomized powder. It is found that for certain dimensional ratios of the preform the die pressure is minimum. An attempt has been made for the determination of the die pressures developed for given geometries of the disc during the closed die forging of polygonal powder preform by using an upper bound approach. Uniform frictional stresses are assumed on top and bottom interfaces and along the interfaces on sides. The feasibility of metal powder preform has been demonstrated by applying an appropriate interfacial friction law and yield criteria. The solution can be extended to closed die forging of any polygonal shape. The results of hexagonal shape is taken for illustration and results so obtained are discussed critically to illustrate the interaction of various process parameters involved and are presented graphically.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Closed Die Forging, Sintering, Preform, Interfacial Friction Law
REFERENCES