Chin-Poh Pang1 and Juh Tzeng Lue 1 1Department of Physics National Tsing Hua University Hsinchu, Taiwan 300, R.O.C.
Received:
July 31, 2003
Accepted:
September 1, 2003
Publication Date:
December 1, 2003
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2003.6.4.01
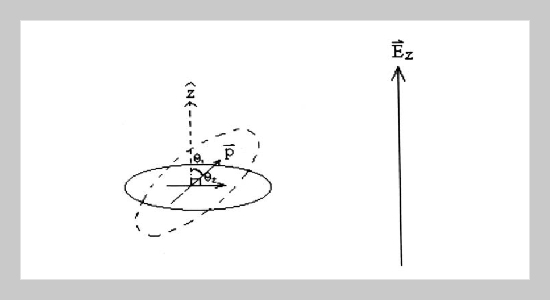
The microscopic structure of a thin liquid crystal film embedded between two glass plates coated with indium-tin–oxide films when applying with electric fields is studied in grand canonical ensemble Monte Carlo simulation. The change of internal enthalpy due to electric dipole-dipole interaction of rod-like nematic liquid crystals is minimized to yield the aligned structure. The time duration to reach the equilibrium state is successfully verified from the direct experimental measurement of light transmissions.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Monte Carlo simulation, Nematic liquid crystals, Field alignment
REFERENCES