Ming-Ren S. Fuh 1 and Hung-Jian Lin1 1Department of Chemistry Soochow University Taipei, Taiwan 111, R.O.C.
Received:
December 18, 2002
Accepted:
January 17, 2003
Publication Date:
March 1, 2003
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2003.6.1.04
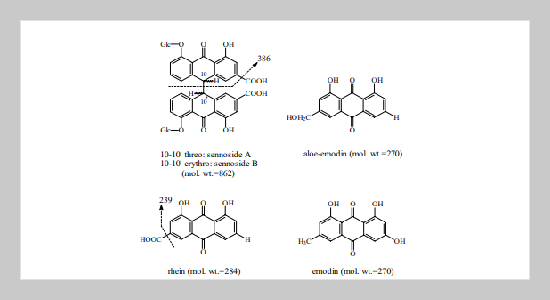
Liquid chromatography-electrospray-mass spectrometry (LC-ES -MS) was employed to analyze five biologically active components (sennoside A and B, rhein, emodin and aloe-emodin) in rhubarb. The separation was achieved on a C18 column using gradient elution. Negative ion detection mode was utilized for ES-MS detection. For sennosides, [M-H]− and a fragmented ion (m/z = 386) were detected. In addition to [M-H]− , [M-COOH]− was observed for rhein. Only one major ion, [M-H]− , was determined for aloe-emodin and emodin. A post-column splitter was employed to enhance the sensitivity of sennoside measurement. Extracted ion monitoring was applied for quantitative analysis. Satisfactory linearity (r2 = 0.99) of each compound was determined. In addition, the content of these five active components in various rhubarb samples were examined by this newly developed LC-ES-MS.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
LC-MS, Chinese Herbal Medicine, Sennoside
REFERENCES