Dan-Yang Qin This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1, Lin Ma1, Xue-Jun Sha1 and Yu-Bin Xu1 1Communication Research Center, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, P.R. China
Received:
May 5, 2009
Accepted:
May 14, 2010
Publication Date:
March 1, 2011
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2011.14.1.09
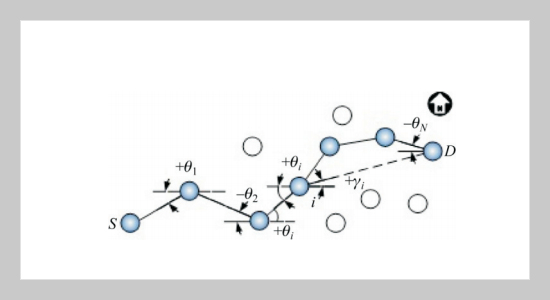
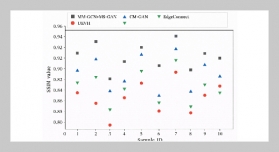
Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET) is a centerless packet radio network without the use of any fixed infrastructure. In recent years, tremendous attentions have been received because of capabilities of self-configuration and self-maintenance especially in public safe and disaster recovery situations. However, attenuation and interference caused by node mobility and wireless channels sharing weaken the stability of communication links, which makes routing protocol design present nontrivial challenges such as broadcast storm, stale route and delay. The negative impact of link-discontinuity on communication is alleviated by an effective survivable routing strategy (SRS) proposed in this paper. SRS is achieved by restricting the route request (RREQ) zone on intermediate forwarding nodes according to the solution of optimal exploring equations. With the purpose of increasing survivability and reducing average end-to-end delay during route maintenance as well as allowing continuous packet forwarding for fault resilience, Network Simulator 2 (NS2) based simulation results show remarkable packets successful delivery rate and the total overhead improvements of this strategy will be obtained.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Mobile Ad Hoc Network, SRS, AODV, Optimal Exploring Model, Beam Method
REFERENCES