Ching-Ming Chao This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1 1Department of Computer and Information Science, Soochow University, Taipei, Taiwan 100, R.O.C.
Received:
July 11, 2006
Accepted:
January 30, 2007
Publication Date:
September 1, 2007
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2007.10.3.10
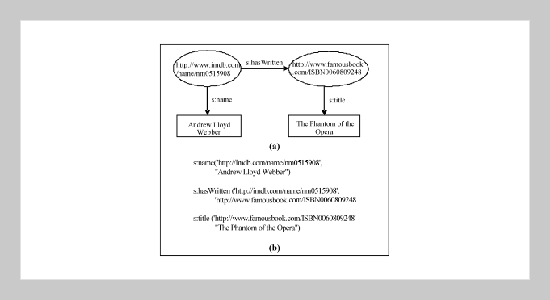
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a foundation for processing metadata, which provides interoperability between applications that exchange machine-understandable information on the World Wide Web (WWW). Because RDF users can use any possible syntax to encode data described in RDF, plus XML possesses the highly flexible hierarchical structure and the machine-independent characteristic, XML has become the most popular way to store and transport RDF documents. Efficient storage and retrieval of XML documents (or, precisely, RDF/XML documents) in persistent data stores has become an important issue in computer technology today. In this paper, therefore, we propose an object-oriented data model, called the RDF Data Store Model (RDSM), for the storage of data extracted from RDF documents, as well as an RDF document decomposition algorithm for the extraction of data from RDF documents. In addition, we propose a generic RDF API that supports fundamental RDF data accessing and querying operations, and utilize the emerging W3C’s SPARQL as the high-level query language for the retrieval of RDF data. Finally, an experimental system is implemented to demonstrate the performance of the proposed approach.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
XML, RDF, RDSM, Generic RDF API, SPARQL
REFERENCES