C. C. Chang This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1, K. P. Chu1 and Y. C. Lai1 1Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan Ocean University Keelung, Taiwan 202, R.O.C.
Received:
January 3, 2005
Accepted:
July 20, 2005
Publication Date:
September 1, 2005
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2005.8.3.04
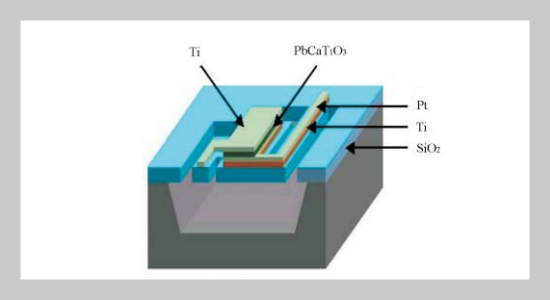
The pyroelectric infrared (PIR) sensor with a calcium-modified lead titanate Pb1-xCaxTiO3 thin film with x = 0.3 [PCT(30)] thin film have been successfully fabricated. A RF planar magnetron sputter was used to deposit PCT(30) thin film. A perovskite thin film can be obtained. From the properties measurement we can obtain the remanent polarization Pr = 25.3 μc/cm2 and coercive electric field Ec = 52.65 KV/cm. The pyroelectric coefficient was measured as a function of temperature which was 4.13 10-4 C/m2K at 300 degree C. For the PIR performance measurement, the voltage response of the single PIR sensor is 723.5 VW-1 and the specific detectivity is 8.28 106 cmW-1 at 0.3 Hz. In addition, a 2-D 8 x 8 element PIR sensor array is finished with fabricated PIR sensors.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Pb0.7Ca0.3TiO3 (PCT(30)), Remanent Polarization, Coercive Electric Field, Pyroelectric Coefficient, Voltage Response, Specific Detectivity
REFERENCES