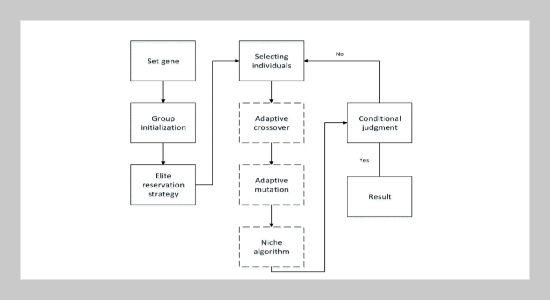
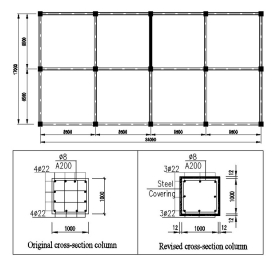
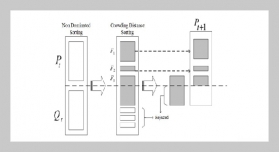
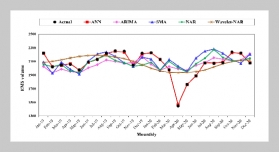
REFERENCES
- [1] Rehman, S. U., Sowerby, K. W. and Coghill, C., “Radio-frequency Fingerprinting for Mitigating Primary User Emulation Attack in Low-end Cognitive Radios,” IET Communications, Vol. 8, No. 8, pp. 1274�1284 (2014). doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2013.0568
- [2] Lei, Y. K., “Individual Communication Transmitter Identification Using Correntropy-based Collaborative Representation,” International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Biomedical Engineering and Informatics. IEEE, pp. 1194�1200 (2017).
- [3] Wen, H., Li, S. Q., Zhu, X. P. and Zhou, L., “A Framework of the PHY-layer Approach to Defense Against Security Threats in Cognitive Radio networks,” IEEE Network, Vol. 27, No. 3, pp. 34�39 (2013). doi: 10. 1109/MNET.2013.6523806
- [4] Zhang, Y., Sun, B. F. and Xiao, J., “Fingerprint Identification Based on Wavelet Transform,” Aeronautical Computing Technique, Vol. 1 (2013). (Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn. 1671-654x.2013.01.001
- [5] Liu, Y. Y., Zheng, L. H. and Liu, H. B., “Individual Transmitter Identification Based on New Feature Parameter of Signal Envelope,” Radio Communications Technology, Vol. 4 (2014). (Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j. issn.1003-3114.2014. 04.022
- [6] Liu, M. W. and Doherty, J. F., “Non linearity Estimation for Specific Emitter Identification in Multipath Channels,” IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, Vol. 6, No. 3, pp. 1076�1085 (2011). doi: 10.1109/SARNOF.2009.4850327
- [7] Taringou, F., Hammi, O. and Srinivasan, B., “Behaviour Modelling of Wideband RF Transmitters Using Hammerstein-Wiener models,” Circuits Devices & Systems Iet, Vol. 4, No. 4, pp. 282–290 (2010). doi: 10. 1049/iet-cds.2009.0258
- [8] Mao, Y. and Ding, F., “A Novel Data Filtering Based Multi-innovation Stochastic Gradient Algorithm for Hammerstein Nonlinear Systems,”Digital Signal Processing, Vol. 46, pp. 215�225 (2015). doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2015.07.002
- [9] Hammi, O., Kedir, A. M. and Ghannouchi, F. M., “Nonuniform Memory Polynomial Behavioral Model for Wireless Transmitters and Power Amplifiers,” Microwave Conference Proceedings (APMC), 2012 AsiaPacific. IEEE, pp. 836–838 (2012).
- [10] Zhou, L., Li, X. and Pan, F., “Gradient-based Iterative Identification for Wiener Nonlinear Systems with Nonuniform Sampling,”Nonlinear Dynamics, Vol. 76, No. 1, pp. 627�634 (2014). doi: 10.1007/s11071-0131156-5
- [11] Abinayadhevi, P. and Prasad, S. J. S., “Identification of pH Process Using Hammerstein-Wiener Model,” Intelligent Systems and Control (ISCO), 2015 IEEE 9th International Conference on. IEEE (2015).
- [12] Talaie, Sharareh, Shoorehdeli and Mahdi Aliyari, “Nonlinear System Identification of Hammerstein Wiener Model Using AWPSO,” Intelligent Systems, Iranian Conference on (2014).
- [13] Yang, F., Chen, Z. and Wei, C., “Nonlinear System Modeling and Identification of Small Helicopter Based on Genetic Algorithm,” International Journal of Intelligent Computing &Cybernetics,Vol.6, No. 1, pp. 45� 61 (2013). doi: 10.1108/17563781311301517
- [14] Barradas, F. M., Cunha, T. R., Lavrador, P. M. and Pedro, J. C., “Polynomials and LUTs in PA Behavioral Modeling: a Fair Theoretical Comparison,” IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, Vol. 62, No. 12, pp. 3274�3285 (2014). doi: 10.1109/TMTT. 2014.2365188
- [15] Song, Q. K., Xu, M. M. and Liu, Y., “WaveletNetwork Controller Based on Improved Genetic Algorithm,” Measurement, Information and Control (ICMIC), 2013 International Conference on. IEEE, pp. 1111�1117 (2013).