Attila Török1, Péter Laborczi This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1 and Balázs Mezny1 1Institute for Applied Telecommunication Technologies, Bay Zoltán Foundation for Applied Research, Fehérvári út 130, H-1116 Budapest, Hungary
Received:
January 8, 2010
Accepted:
February 25, 2010
Publication Date:
March 1, 2010
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2010.13.1.06
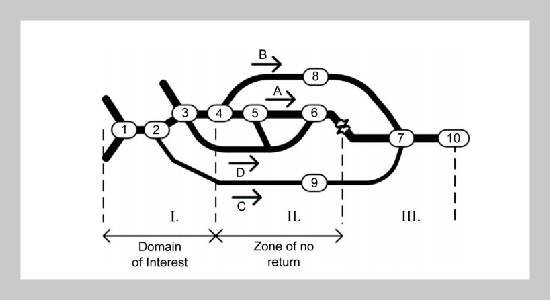
Traffic information in vehicular ad hoc networks is distributed through intelligent flooding mechanisms. To cope with superfluous forwarding usually rate- or spatial-adaptivity is introduced in the dissemination protocols. This paper focuses on spatial adaptivity techniques, which in certain cases should use context-aware information to achieve good performance. We propose an Integer Linear Programming (ILP) formulation to calculate on a digital map the Domain of Interest (DoI), the area where information about traffic jams is important for drivers. Afterwards, we analytically investigate the effect of this spatial context-awareness on traffic information dissemination. The behavior of a flooding protocol using the DoI knowledge is also explored through extensive simulations. Important characteristics on spatial adaptivity regarding the information dissemination strategies are concluded from the analytical and simulation results.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Intelligent Transportation Systems, Traffic Congestion, Information Dissemination, Communication Protocols, Linear Programming, Optimization
REFERENCES