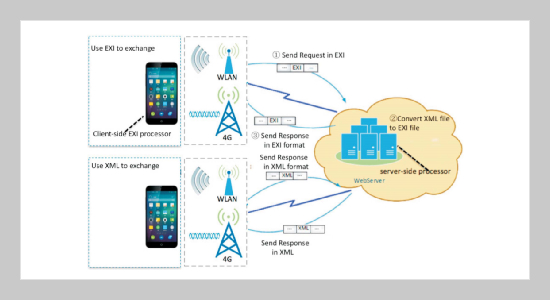
REFERENCES
- [1] Information on: http://www.w3.org/TR/exi.
- [2] Information on: http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/WD-xbcuse-cases-20041109/.
- [3] Marcelo, A., Pablo, B. and Leonid, L., 1st ed., XMLManaging Data Exchange, Morgan and Claypool Publishers (2011).
- [4] Hossam, J., Paul, R. and Jocelyne, P., “An XML-based Framework for Automating Data Exchange in Healthcare,” Proc. of 2010 IEEE International Conference on e-Health Networking Applications and Services, Lyon, France, July 1�3, pp. 264�269 (2010). doi: 10.1109/ HEALTH.2010.5556559
- [5] Harrusi, S., Averbuch, A. and Yehudai, A., “XML Syntax Conscious Compression,” Proc. of 2010 IEEE International Conference on Data Compression Conference, March 1�3, California, U.S.A., pp. 402�411 (2010). doi: 10.1109/DCC.2006.85
- [6] Lars, J., Dinko, H. and Trude, H., “Efficient Web Services in Mobile Networks,” Proc. of 2008 European Conference on Web Services, Dublin, Ireland, Nov. 12�14, pp. 197�204 (2008). doi: 10.1109/ECOWS. 2008.24
- [7] Wang, L., Mutafungwa, E., Puvvala, Y. and Manner, J., “Strategies for Energy-efficient Mobile Web Access: an East African Case Study,” e-Infrastructure and e-Services for Developing Countries, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 74–83 (2012). doi: 10.1007/ 978-3-642-29093-0_7
- [8] �liwa, J., Podlasek, T. and Amanowicz, M., “Web Services Efficiency in Disadvantaged Environment,” Journal of Telecommunications and Information Technology, No. 1, pp. 62�68 (2001).
- [9] Castellani,A. P., Bui,N., Casari,P. and Rossi,M.,“Architecture and Protocols for the Internet of Things-A Case Study,” Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops, Mar. 29�Apr. 2, Mannheim, Germany, pp. 678�683 (2010). doi: 10.1109/PERCOMW. 2010.5470520
- [10] Li, J., AResearch of EXI-based Web Service Optimization Approach, Master, Desertation, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China (2010).
- [11] Moritz, G., Golatowski, F. and Timmermann, D., “A Lightweight SOAP over CoAP Transport Binding for Resource Constraint Networks,” IEEE, International Conference on Mobile Ad hoc and Sensor Systems, MASS 2011, Valencia, Spain, October 17�22, pp. 861�866 (2011). doi: 10.1109/MASS.2011.101
- [12] Information on: http://exificient.sourceforge.net/.
- [13] Käbisch, S., Peintner, D., Heuer, J. and Kosch, H., “Efficient and Flexible XML-based Data-exchange in Microcontroller-based Sensor Actor Networks,” Proc. of IEEE International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops, Perth, Australia, Apr. 20�13, pp. 508�513 (2010). doi: 10.1109/WAINA.2010.95
- [14] Debich, S. J., The Role of Efficient XML Interchange (EXI) in Navy Wide-area Network (WAN) Optimization [R]. Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA (2015).
- [15] Xie, X. Y., Wang, H. and Chen, Y. P., “Performance Evaluation of Efficient xml Interchange in Resource restricted Network,” Computer Technology and Development, Vol. 23, No. 6, pp. 54�58 (2013). [16] Information on: http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns/.
- [17] Shi, Y. H. and Shu-Yu, L. I., “Research of Data Exchange Model Based on Dynamic Service,” Application Research of Computers, Vol. 28, No. 12, pp. 4576�4580 (2011).
- [18] Chen, S. B., “Modeling and Verifying Web Applications,” Ph.D. Desertation, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China (2009).
- [19] Information on: http://a.vmall.com/app/C10542084.